Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (41): 6585-6590.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.41.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Recombinant CXCR4 gene lentivirus transfection of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro
Cao Zhi-qiang, Wang Yang, Liu Long
- Department of Urinary, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Command, Shenyang 110840, Liaoning Province, China
-
Revised:2014-09-18Online:2014-10-01Published:2014-10-01 -
Contact:Liu Long, Master, Chief physician, Department of Urinary, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Command, Shenyang 110840, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Cao Zhi-qiang, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Urinary, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Command, Shenyang 110840, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, No. 2013020199
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cao Zhi-qiang, Wang Yang, Liu Long. Recombinant CXCR4 gene lentivirus transfection of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6585-6590.
share this article
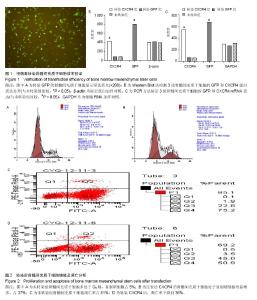
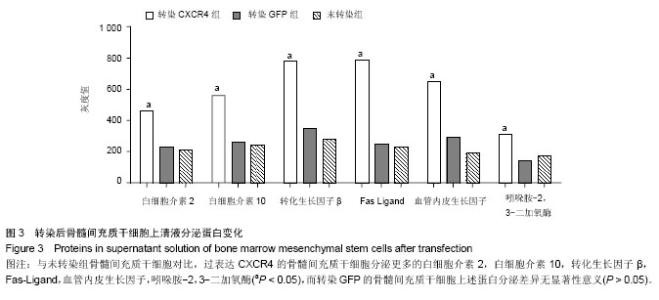
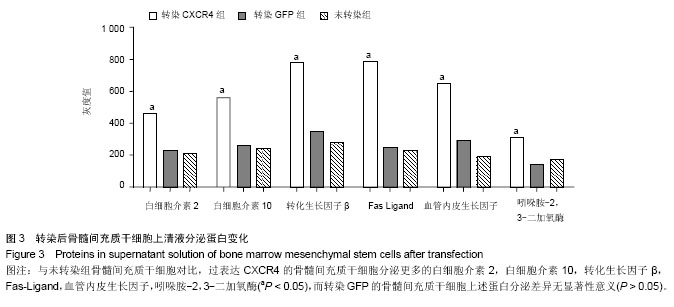
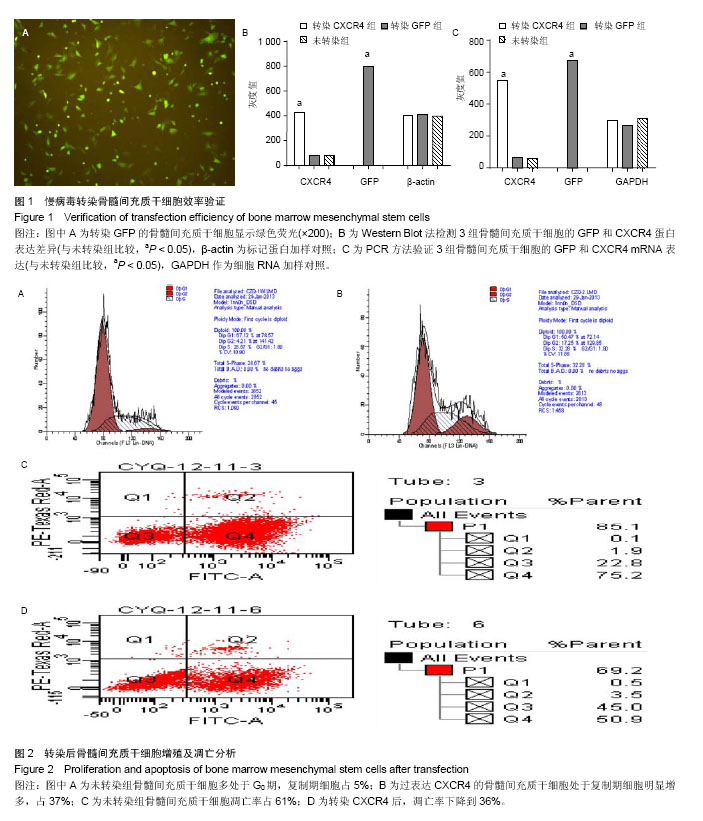
2.1 转染效率分析 骨髓间充质干细胞转染靶基因CXCR4或GFP。两组实验方案、实验条件完全一致,所以,转GFP组在荧光显微镜下观察绿色荧光作为转染效率的定性检查,见图1A,Western Blot方法在蛋白水平验证各组GFP和CXCR4蛋白的表达情况,见图1B。RT-PCR法在mRNA水平上再次验证转染效率成功(图1 C),转染CXCR4组表达CXCR4最高,转染GFP组表达GFP最高(P < 0.05)。 2.2 转染后骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及凋亡分析 经慢病毒转染不同基因进入骨髓间充质干细胞后,为了验证病毒转染是否影响骨髓间充质干细胞自身生物特性,实验测定了转染CXCR4组和未转染组细胞的细胞周期和凋亡率(图2)。结果发现,转染CXCR4而过表达CXCR4后的骨髓间充质干细胞生长状态良好,流式细胞仪检测处于复制期的骨髓间充质干细胞明显增多,而凋亡细胞明显减少,提示CXCR4具有促增殖和抗凋亡作用(P < 0.05)。 2.3 转染后骨髓间充质干细胞上清液分泌蛋白变化 经慢病毒转染不同基因进入骨髓间充质干细胞后,为了验证病毒转染是否影响骨髓间充质干细胞的蛋白分泌,实验测定了各组细胞培养上清中分泌蛋白水平变化,过表达CXCR4后的骨髓间充质干细胞分泌蛋白水平发生变化,测定的白细胞介素2,白细胞介素10,转化生长因子β,Fas-Ligand,血管内皮生长因子,吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶水平均呈上调趋势(P < 0.05,图3)。"
| [1] Yamaguchi S, Kuroda S, Kobayashi H,et al.The effects of neuronal induction on gene expression profile in bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC)--a preliminary study using microarray analysis.Brain Res. 2006;1087(1):15-27. [2] 宋晨阳,徐皓,陈建梅,等.静脉移植CXCR-4基因转染骨髓间充质干细胞在脊髓损伤鼠体内的迁移与分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(23):4316-4320. [3] 郑栋,郭军. SDF-1/CXCR4信号轴介导的骨髓间充质干细胞治疗心力衰竭的研究进展[J]. 心脏杂志,2014,26(6):730-733. [4] 宗阿南,郑志红,史晓萍,等.探讨《关于善待实验动物的指导性意见》饲育、应用、运输及相关方面的措施[J]. 实验动物科学, 2008,25(2):63-64,67. [5] Rankin SM.Chemokines and adult bone marrow stem cells. Immunol Lett. 2012;145(1-2):47-54. [6] Li J, Lepadatu AM, Zhu Y,et al.Examination of structure-activity relationship of viologen-based dendrimers as CXCR4 antagonists and gene carriers.Bioconjug Chem. 2014;25(5):907-917. [7] Bot I, Daissormont IT, Zernecke A,et al.CXCR4 blockade induces atherosclerosis by affecting neutrophil function.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;74:44-52. [8] Wynn RF, Hart CA, Corradi-Perini C,et al.A small proportion of mesenchymal stem cells strongly expresses functionally active CXCR4 receptor capable of promoting migration to bone marrow.Blood. 2004;104(9):2643-2645. [9] Liu L, Yu Q, Lin J,et al.Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is essential for hypoxia-induced mesenchymal stem cell mobilization into the peripheral blood.Stem Cells Dev. 2011; 20(11):1961-1971. [10] Maijenburg MW, van der Schoot CE, Voermans C.Mesenchymal stromal cell migration: possibilities to improve cellular therapy.Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(1):19-29. [11] Kean TJ, Lin P, Caplan AI, et al.MSCs: Delivery Routes and Engraftment, Cell-Targeting Strategies, and Immune Modulation. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:732742. [12] Lau TT, Wang DA.Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1): homing factor for engineered regenerative medicine.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2011;11(2):189-197. [13] Xinaris C, Morigi M, Benedetti V,et al.A novel strategy to enhance mesenchymal stem cell migration capacity and promote tissue repair in an injury specific fashion.Cell Transplant. 2013;22(3):423-436. [14] 孙欣慰,杨铧琦,徐惠成. 17β-雌二醇通过上调CXCR4表达促进骨髓间充质干细胞的趋化迁移[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2014, 36(7):664-668. [15] Xie J, Wang H, Song T,et al.Tanshinone IIA and astragaloside IV promote the migration of mesenchymal stem cells by up-regulation of CXCR4.Protoplasma. 2013;250(2):521-530. [16] Zhao Z, Watt C, Karystinou A,et al.Directed migration of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a physiological direct current electric field.Eur Cell Mater. 2011; 22:344-358. [17] Burks SR, Ziadloo A, Kim SJ,et al. Noninvasive pulsed focused ultrasound allows spatiotemporal control of targeted homing for multiple stem cell types in murine skeletal muscle and the magnitude of cell homing can be increased through repeated applications.Stem Cells. 2013;31(11):2551-2560. [18] Yuan L, Sakamoto N, Song G,et al.Low-level shear stress induces human mesenchymal stem cell migration through the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis via MAPK signaling pathways.Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(17):2384-2393. [19] Lehwald N, Duhme C, Wildner M,et al.HGF and SDF-1-mediated mobilization of CD133+ BMSC for hepatic regeneration following extensive liver resection.Liver Int. 2014; 34(1):89-101. [20] 刘星星,范恒,段雪云,等. SDF-1α/CXCR4轴促进间充质干细胞归巢于实验性结肠炎受损结肠[J].世界华人消化杂志,2013, 21(33):3623-3630. [21] Bobis-Wozowicz S, Miekus K, Wybieralska E,et al.Genetically modified adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing CXCR4 display increased motility, invasiveness, and homing to bone marrow of NOD/SCID mice.Exp Hematol. 2011;39(6):686-696.e4. [22] Cheng Z, Ou L, Zhou X,et al.Targeted migration of mesenchymal stem cells modified with CXCR4 gene to infarcted myocardium improves cardiac performance.Mol Ther. 2008;16(3):571-579. [23] Gul-Uludag H, Xu P, Marquez-Curtis LA,et al.Cationic liposome-mediated CXCR4 gene delivery into hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells: implications for clinical transplantation and gene therapy.Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(10):1587-1596. [24] Marquez-Curtis LA, Gul-Uludag H, Xu P,et al.CXCR4 transfection of cord blood mesenchymal stromal cells with the use of cationic liposome enhances their migration toward stromal cell-derived factor-1.Cytotherapy. 2013;15(7): 840-849. [25] Madeira C, Mendes RD, Ribeiro SC, et al.Nonviral gene delivery to mesenchymal stem cells using cationic liposomes for gene and cell therapy.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010: 735349. [26] Wiehe JM, Kaya Z, Homann JM,et al.GMP-adapted overexpression of CXCR4 in human mesenchymal stem cells for cardiac repair.Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(5):2073-2081. [27] Pan S, Wan JZ, Liu SS, et al. Lentivirus carrying the Atoh1 gene infects normal rat cochlea. Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8(17): 1551-1559. [28] Dong L, Han CX,Zhang HZ, et al. Construction of a recombinant lentivirus containing human microRNA-7-3 and its inhibitory effects on glioma proliferation. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(27): 2144-2150. [29] Ren J, Jin P, Sabatino M,et al.Global transcriptome analysis of human bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) reveals proliferative, mobile and interactive cells that produce abundant extracellular matrix proteins, some of which may affect BMSC potency.Cytotherapy. 2011;13(6):661-674. [30] Cui X, Chopp M, Zacharek A,et al.Chemokine, vascular and therapeutic effects of combination Simvastatin and BMSC treatment of stroke.Neurobiol Dis. 2009;36(1):35-41. [31] Zeng D, Hao L, Xu W,et al.Pinch-1 was up-regulated in leukemia BMSC and its possible effect.Clin Exp Med. 2013; 13(1):21-27. [32] 薛武军,李旭,郭奇,等. 监测肾移植术后IL-2和sIL-2R的变化及其意义[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志,1995,16(3):148-149,190. [33] 傅颖媛,王斌,冯练强.同种异体肾移植者与正常人NK细胞活性及IL-2R的研究[J]. 江西医学院学报,1993,33(4):16-18. [34] 黄萱,热衣汗,孙岩,等.急性肾排斥反应时IFN-γ和IL-10的表达及意义[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2010,26(5):484-486. [35] 毕树雄,戴尅戎,汤亭亭. IL-4与IL-10联合诱导异种骨移植免疫耐受的实验研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(15): 1174-1178. [36] 芮晓晖,蔡端,张群华,等. TNF-α和IL-10在非协调性异种肝移植中的作用探讨[J]. 中华肝胆外科杂志,2002,8(11):680-682. [37] 宋艳玲,赖天宝,李嫚,等. VEGF基因修饰MSCs移植对脑梗死大鼠血管源性机制的实验研究[J]. 卒中与神经疾病,2011,18(6): 323-325,370. [38] 王晓艳,苏又苏,谢培益,等. VEGF基因转染同种异体骨髓间充质干细胞对心肌梗死的治疗作用[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2008,6(10):1177-1178. [39] 杨宝宏,于津浦,李慧,等. 乳腺癌髓系来源抑制细胞中IDO对T淋巴细胞免疫抑制作用初探[J]. 中国肿瘤临床,2012,39(9): 506-509. [40] 徐鹏,葛海燕. TGF-α对人脂肪来源干细胞Survivin蛋白的影响[J]. 同济大学学报:医学版,2013,34(1):17-20. [41] Casiraghi F, Perico N, Remuzzi G.Mesenchymal stromal cells to promote solid organ transplantation tolerance.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2013;18(1):51-58. [42] Rosborough BR, Raïch-Regué D, Turnquist HR,et al.Regulatory myeloid cells in transplantation.Transplantation. 2014;97(4):367-379. |
| [1] | Wang Jian-ji, Yang Long, Li Jing, Sun Qi, Zuo Wei-min, Ren Qi-feng, Sun Yu, Wu Zhan-yu, Zou Qiang, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Development and application of special-purpose grafter by femoral head decompression combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation based on three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6636-6642. |
| [2] | Zhou Chang-yan, Zhou Qing-huan, Bian Jing, Chen Ke, Chen Wen. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with calcium phosphate cement to repair articular cartilage defects in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1195-1199. |
| [3] | Jing Cai-xia, Liu Chang-kui, Tan Xin-ying, Luo Jin-chao, Hu Min. Bone mesenchymal stem cells with allogeneic bone to repair canine mandibular defects: detection of osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2138-2143. |
| [4] | Xu Xiang, Yin He-ping. Platelet-rich plasma accelerates the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2144-2148. |
| [5] | Zhao Xiao-jian, Lu Cai-ping, Chu Wei-wei, Zhang Ya-xiao, Zhang Bing, Zhen Qiang, Tan Guo-liang, Wang Ren-feng, Liu Jia-bao, Wu Lin. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treatment of emphysema: intravenous versus intratracheal approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2211-2215. |
| [6] | Liang Jian-ji, He Zhi-yong, Liu Kang, Li Xiao-ling, Cheng Wei-min, Yu Xin-ping, Chen Er-dong. Intraarticular injection of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for mild-to-moderate osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2216-2223. |
| [7] | Gao Zhuo-yue, Liu Yong-qi, He Jian-xin, Wu Zhi-wei, Luo Ya-li, Su Yun, Zhang Li-ying, Zhang Qi, Wu You-ming, Zhou Ni-na. Regulatory effects of warming yang and invigorating qi treatment on the inflammatory balance and genetic stability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under tumor microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2267-2272. |
| [8] | Zhao Jia, Sun Jian-ping, Gao Yan-xia, Tang Ni-na, Niu Meng, Cui Meng, Han Xiao-qing, Sui Ai-hua . Platelet-derived growth factor-DD induces the proliferation and differentiation of rat renal fibroblasts into myofibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1688-1693. |
| [9] | Han Xiang-zhen, He Hui-yu, Hu Yang, Ba Jiao-jiao, Wang Huan-huan, Mi Xue, Abulizi•Abudula. Recombinant lentiviral vector transfected sheep bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteogenic gene expression changes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 821-828. |
| [10] | Huang Jian-feng, Huang Ji-feng, Zhang Wei-cai. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into neuron-like cells induced by combination of two cytokines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 829-834. |
| [11] | Zou Bin, Zong Shao-hui, Zeng Gao-feng, Fang Ye, Gao Tai-hang. Effects of alpha-zearalanol on the osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 835-840. |
| [12] | Yang Yi, Ding Wen-jing, Dong Wan-li. Autophagy-related gene Beclin-1 expression in neuron-like differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 841-846. |
| [13] | Su Xue-lian, Bao Guang-jie, Kang Hong, Liu Lin, Kong Nan-nan. Morphological changes of goat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into fibrochondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 860-865. |
| [14] | Nie De-zhi, Wan Ying, Ben Liang, Wang Ying-jun, Liu Xiang-zhu, Wang Li-hui, Li Chao, Zhang Shi-dong. Stem cell tumorigenicity in Balb/c nude mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 888-893. |
| [15] | Fan Yan, Wang Jian-jun, Wei Feng, Fan Xiao-hai, Ma Ai-qun. Effect of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on inflammatory response and ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 900-905. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||